Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay or cavities, is a prevalent dental problem caused by the demineralization of tooth enamel due to bacterial activity. Traditional caries removal methods involve using dental drills to mechanically remove decayed tooth structure. However, chemo-mechanical caries removal (CMCR) offers an innovative and minimally invasive approach to address this issue.
Chemo-mechanical caries removal is an alternative method that combines the use of specialized chemicals and gentle mechanical means to dissolve and remove carious tissue from teeth. This technique is particularly valuable in pediatric dentistry and for anxious patients who may experience discomfort during conventional drilling procedures. Chemo-mechanical caries removal holds significant importance in modern dentistry due to several advantages it offers:
- Minimally Invasive Approach: CMCR reduces the need for aggressive drilling, preserving more healthy tooth structure and minimizing patient discomfort during the procedure.
- Anxiety Reduction: The gentle and noiseless nature of CMCR appeals to patients with dental anxiety, creating a more pleasant and relaxed dental experience.
- Pulp Vitality Preservation: CMCR minimizes the risk of pulp exposure, reducing the likelihood of pulp inflammation and the need for subsequent root canal treatments.
- High Efficacy: Chemo-mechanical caries removers have been shown to effectively remove carious tissue, maintaining tooth integrity and function.
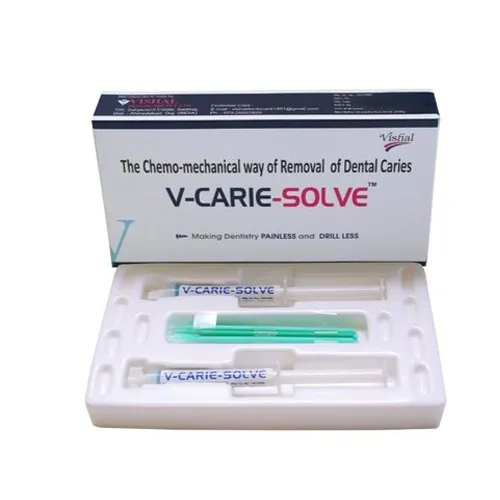
Chemo-mechanical caries removers typically consist of a gel or paste containing a combination of acids and other active agents. These agents work synergistically to dissolve the softened carious dentin, making it easier for gentle mechanical means like hand instruments to remove the decayed tissue without causing trauma to the tooth. Dentalkart proudly presents a comprehensive category of chemo-mechanical caries removers, catering to the diverse needs of dental professionals. Featuring renowned brands such as Vishal and Kids-e-Dental, Dentalkart ensures the availability of high-quality and reliable CMCR products.
Dentalkart's selection includes a variety of chemo-mechanical caries removers suitable for both adult and pediatric patients, making it a one-stop destination for dental professionals seeking effective and minimally invasive alternatives for dental caries removal. With Dentalkart's commitment to offering genuine and authentic products, dental practitioners can confidently choose the most suitable chemo-mechanical caries removers for their patients, promoting superior dental care and patient satisfaction.
Q: What is chemo mechanical caries remover?
A: Chemo-mechanical caries remover is a minimally invasive dental technique that uses chemicals and gentle mechanical means to dissolve and remove dental caries (decay) from teeth, reducing the need for aggressive drilling and preserving more healthy tooth structure. It is an innovative approach particularly suitable for pediatric dentistry and anxious patients, providing a more comfortable dental experience.
Q: How does CEMO work?
A: Chemo-mechanical caries removal (CEMO) works by applying a specialized gel or paste with mild acids to the carious tooth surface, softening and dissolving the decayed dentin. Gentle mechanical instruments are then used to remove the softened caries while preserving healthy tooth structure. CEMO is minimally invasive, suitable for pediatric patients, and reduces discomfort and noise compared to traditional drilling methods.
Q: Can chemo-mechanical caries removal be used for all carious lesions, or are there specific indications and contraindications?
A: CEMO is indicated for most carious lesions, especially in enamel and shallow dentin caries. However, it may not be suitable for deep dentin caries or cases with extensive decay. Understanding the indications and contraindications is crucial to make informed treatment decisions.
Q: Can CEMO be combined with other caries removal techniques or restorative procedures for more complex cases?
A: Yes, CEMO can be combined with other techniques, such as selective excavation or traditional drilling, to address more complex cases. Dentists can tailor the treatment plan to suit individual patient needs and achieve optimal clinical outcomes.
Q: Is chemo-mechanical caries removal suitable for non-carious cervical lesions (NCCLs), and if so, how does it differ from caries removal in enamel and dentin lesions?
A: CEMO can be used for NCCLs involving demineralized tooth structure. The approach involves selectively removing demineralized and undermined tissue from the lesion, promoting better bonding of restorative materials and reducing the risk of restoration failure.